- ea is not working on all accounts
- Values in MT4 and MT5 Differ?
- real time feeds in demo
There are different types of brokers. I collected some links/video etc:
Forum on trading, automated trading systems and testing trading strategies
Broker's ; Are they with "zero-sum game" or "try their best" going to turn the market towards ?
newdigital, 2013.06.03 12:42
I did not understand sorry :) Are you talking about dealing desk brokers (DD) and non-dealing desk (NDD) broker?
- DD brokers are mediating between us (traders) and the banks (liquidity providers), and because of that - DD brokers are making the market for us (for traders) controlling the market we are trading with (them).
- NDD brokers are not mediating, that the traders are placing the orders directly to real market.
But people say that there are no so much differences between them concerning the traders' opinion ... "brokers are not our friends" - this is usual slogan which you can meet everywhere :)
My opinion: if you place stop loss and/or take profit so brokers can do nothing (not "sum zero game"; and not "try their best") ... nothing ... because tp or sl are executed by data, and datafeed is provided by broker, and this datafeed are slightly6 dofferent from one broker to an other one ... so, some traders are making EA or signal for some particular broker.
Example with some talking between traders:
- one trader: "I created good EA and it is performing very good with trading"
- second trader: "performing in good way? that's fine. which broker?"
So, it is usual questions ...
=======
As I said - hidden sl/tp is used with complex systems which are based on many indicators and one EA is trading for many pairs taking onto considerationmany timeframes on the same time (MTF EAs). Those kind of EAs are using hidden tp/sl and/or tp/sl which were coded inside the code of the EA. But irrespective off - those EAs are using hard tp/sl just in case of electricity will be switched off and so on (because hidden/coded tp/sl is not executed on the brokers' server; but hard tp/sl is directly executed on the brokers' server even if you will close your Metatrader for example).
Forum on trading, automated trading systems and testing trading strategies
Something Interesting in Financial Video August 2013
newdigital, 2013.08.25 15:16
81. The Role of the Retail Forex BrokerBefore the internet, very few individuals traded foreign exchange as they could not get access to a level of pricing that would allow them a reasonable chance to profit after transaction costs. Shortly after the internet became mainstream however several firms built online trading platforms which gave the individual trader a much higher level access to the market. The internet introduced two main features into the equation which were not present before:
1. Streaming Quotes: The Internet allowed these firms to stream quotes directly to traders and then have them execute on those quotes from their computer instead of having to deal over the phone. This automated trade processing, and therefore made it easier for firms to offer the ability to trade fx to the individuals and still be profitable.
2. Automatic Margin Calls: What is not so obvious but what was perhaps even more key is that the internet allowed an automated margin call feature to be built into the platform. This allowed firms to accept cash deposits from clients instead of having to put them through the process of signing up to trade via a credit line. As we discussed in our last lesson it is very difficult to get a credit line to trade FX and for those who do it is a lot of paperwork and hoops to jump through before they can begin trading. This would have made it impossible to offer FX trading to smaller individual traders as the cost involved in getting them set up to trade would not be worth it.
As the electronic platform allowed clients to deposit funds and then automatically cut them out of positions if they got to low on funds, this negated the need for credit lines and made the work to get an individual account open well worth it to the forex broker from a profit standpoint.
If you don't understand all the ins and outs of margin at this point don't worry as this is something that we are going to go into much more detail on in a later lesson.
For now it is simply important to understand that what these firms did was take all the traders who were not big enough by themselves to get access to good pricing and routed their order flow through one entity that was. This allowed these firms access to much tighter pricing than would otherwise have been possible which was then passed along plus a little for the brokers to the end client.
So now you can see why although the forex market has been around for a relatively long period of time, individuals have only started to trade the market over the last few years.
Anther key thing that it is important to understand here is that the larger a firm gets in terms of trading volume, the greater access that firm has to tighter prices and liquidity and the more likely that firm is to be able to pass on better pricing and execution to their clients.
Forum on trading, automated trading systems and testing trading strategies
Something Interesting in Financial Video October 2014
newdigital, 2014.10.17 20:03
Difference between ECN, market makers and STP brokers
In a perfect world the cost of buying and selling currencies would be
the same, no matter which Forex broker you use. Unlike the stock market
where we get heavy regulation and where stock prices are derived from a
single exchange, prices vary from different Forex broker platforms.
The
reason why is because currency prices are derived from the Interbank
market which is a conglomerate of banks and hedge funds that provide
prices to various Forex brokers around the world. The better the
relationship between the Interbank market participants and the broker
means that the prices are cheaper.
We expand on this in the video
tutorial whilst also describing the main difference between ECN, market
makers and STP Forex brokers.
Forum on trading, automated trading systems and testing trading strategies
newdigital, 2013.07.01 06:59
Just something about ECN and STP - The Truth about Currenex Brokers :
===========
What is an ECN?
ECN is a term often used when referring to Currenex. ECN stands for
Electronic Communication Network and it eliminates the function of a
third party in the execution of orders. Without the intercession of a
third party, market participants of any size can interact directly for
Bid and Offer prices posted by other market participants. This leads to
greater transparency and narrower spreads. ARCHIPELAGO, purchased by
the NYSE in 2006, and ISLAND are two well known ECNs.
What is an ESP?
ESP™ means Executable Streaming Prices and is offered through the
Currenex system. Currenex connects to multiple sources of liquidity,
primarily banks, who offer "pools of liquidity". This expansiveness
from the multiple pools of liquidity, available through Currenex’s ESP,
provides better price discovery and narrower spreads for traders.
The prices that are offered via Currenex are executed directly within these various pools of liquidity. Whereas in the past, a trader would be required to obtain a Prime Brokerage relationship with one or more of the major liquidity providers which required a very high threshold and associated high expenses.
Not all Currenex Brokers are the same.
It is important to remember that a broker’s Currenex offering is only as good as the liquidity sources that are linked to the platform. The quantity and quality of liquidity sources can lead to dramatic differences in price spreads. For instance, a broker offering 1-2 banks versus a broker offering 8-10 banks will have a dramatic difference in pricing and liquidity.
What is STP?
STP, or Straight Through Processing, is a term commonly used among Forex
brokers.Many Forex brokers state they use "interbank pricing" but act
as a counter party to their customers’ trades. They take the other side
of the trade, going against the client’s best interest, and make money
on a client’s losing trade.
Conversely, a true STP setup passes the order in an automated way to all
liquidity sources. With a true STP broker, there is not the
possibility of any adversarial relationship between the broker and
client as the broker only generates revenue in the form of a commission
per trade rather than the dealing desk model of capturing client losses.
Forum on trading, automated trading systems and testing trading strategies
newdigital, 2013.07.01 07:19
Just next educational article about ECN and so on - Market Makers Vs. Electronic Communications Networks
===============
The foreign exchange market (forex or FX) is an unregulated global market in which trading does not occur on an exchange and does not have a physical address of doing business. Unlike equities, which are traded through exchanges worldwide, such as the New York Stock Exchange or the London Stock Exchange, foreign exchange transactions take place over-the-counter (OTC) between agreeable buyers and sellers from all over the world. This network of market participants is not centralized, therefore, the exchange rate of any currency pair at any one time can vary from one broker to another.
How Market Makers Work
Market makers "make" or set both the bid and the ask prices on their systems and display them publicly on their quote screens. They stand prepared to make transactions at these prices with their customers, who range from banks to retail forex traders. In doing this, market makers provide some liquidity to the market. As counterparties to each forex transaction in terms of pricing, market makers must take the opposite side of your trade. In other words, whenever you sell, they must buy from you, and vice versa.
The exchange rates that market makers set, are based on their own best interests. On paper, the way they generate profits for the company through their market-making activities, is with the spread that is charged to their customers. The spread is the difference between the bid and the ask price, and is often fixed by each market maker. Usually, spreads are kept fairly reasonable as a result of the stiff competition between numerous market makers. As counterparties, many of them will then try to hedge, or cover, your order by passing it on to someone else. There are also times in which market makers may decide to hold your order and trade against you.
There are two main types of market makers: retail and institutional. Institutional market makers can be banks or other large corporations that usually offer a bid/ask quote to other banks, institutions, ECNs or even retail market makers. Retail market makers are usually companies dedicated to offering retail forex trading services to individual traders.
Pros:
- The trading platform usually comes with free charting software and news feeds. (For related reading, see Forex: Demo Before You Dive In.)
- Some of them have more user-friendly trading platforms.
- Currency price movements can be less volatile, compared to currency prices quoted on ECNs, although this can be a disadvantage to scalpers.
Cons:
- Market makers can present a clear conflict of interest in order execution, because they may trade against you.
- They may display worse bid/ask prices than what you could get from another market maker or ECN.
- It is possible for market makers to manipulate currency prices to run their customers' stops or not let customers' trades reach profit objectives. Market makers may also move their currency quotes 10 to 15 pips away from other market rates.
- A huge amount of slippage can occur when news is released. Market makers' quote display and order placing systems may also "freeze" during times of high market volatility.
- Many market makers frown on scalping practices and have a tendency to put scalpers on "manual execution," which means their orders may not get filled at the prices they want.
How ECNs Work
ECNs pass on prices from multiple market participants, such as banks and market makers, as well as other traders connected to the ECN, and display the best bid/ask quotes on their trading platforms based on these prices. ECN-type brokers also serve as counterparties to forex transactions, but they operate on a settlement, rather than pricing basis. Unlike fixed spreads, which are offered by some market makers, spreads of currency pairs vary on ECNs, depending on the pair's trading activities. During very active trading periods, you can sometimes get no ECN spread at all, particularly in very liquid currency pairs such as the majors (EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD and USD/CHF) and some currency crosses.
Electronic networks make money by charging customers a fixed commission for each transaction. Authentic ECNs do not play any role in making or setting prices, therefore, the risks of price manipulation are reduced for retail traders. (For more insight, see Direct Access Trading Systems.)
Just like with market makers, there are also two main types of ECNs: retail and institutional. Institutional ECNs relay the best bid/ask from many institutional market makers such as banks, to other banks and institutions such as hedge funds or large corporations. Retail ECNs, on the other hand, offer quotes from a few banks and other traders on the ECN to the retail trader.
Pros:
- You can usually get better bid/ask prices because they are derived from several sources.
- It is possible to trade on prices that have very little or no spread at certain times.
- Genuine ECN brokers will not trade against you, as they will pass on your orders to a bank or another customer on the opposite side of the transaction.
- Prices may be more volatile, which will be better for scalping purposes.
- Since you are able to offer a price between the bid and ask, you can take on the role as a market maker to other traders on the ECN.
Cons:
- Many of them do not offer integrated charting and news feeds.
- Their trading platforms tend to be less user-friendly.
- It may be more difficult to calculate stop-loss and breakeven points in pips in advance, because of variable spreads between the bid and the ask prices.
- Traders have to pay commissions for each transaction.
The Bottom Line
The type of broker that you use can significantly impact your trading performance. If a broker does not execute your trades in a timely fashion at the price you want, what could have been a good trading opportunity can quickly turn into an unexpected loss; therefore, it is important that you carefully weigh the pros and cons of each broker before deciding which one to trade through.
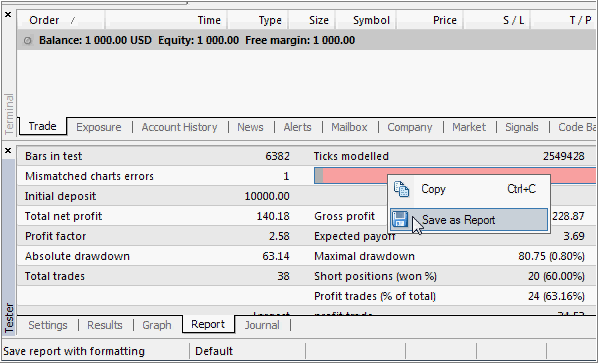
After test finished - 'Report' - right mouse click and 'Save as Report' - see image:
- Free trading apps
- Over 8,000 signals for copying
- Economic news for exploring financial markets
You agree to website policy and terms of use